HOME :: The Role of Microlearning in Empowering The Workforce
A Comprehensive Guide to Microlearning
A culture of continuous learning in the workplace creates huge advantages for organizations. So, dive into this vast reservoir of knowledge to understand the power that Microlearning can have on training outcomes. From learning strategies to understanding Learning and Performance Ecosystems, we’ve got all the answers you need to enhance your training effectiveness.
1
What is Microlearning?
Microlearning is a form of brief, bite-sized learning that features short learning nuggets. The training can be delivered via a standalone nugget, with each nugget intended to cater to specific outcomes, or as multiple nuggets that provide a learning journey.
This approach is not just about breaking down a 10-hour training program into small chunks. It’s also an action-oriented approach to offer bite-sized learning that encourages learners to acquire knowledge, take action, and practice learning. A recommended approach to create Microlearning nuggets is to first pinpoint a broader learning goal and then slice it down into micro components.
Microlearning proves most efficient when employed to provide training within the learner’s flow of work. It serves as a versatile solution for various corporate training requirements, encompassing Formal Training, Performance Support Tools, just-in-time learning aids, skill practice, proficiency enhancement, problem-solving challenges, review and retention, and fostering Social Learning and Self-Directed Learning.
2
Microlearning Theory – Why Microlearning Works?
In a world that is full of distractions and increasingly shorter attention spans, it becomes essential to provide concise, targeted learning modules. These modules are the key to capturing learners’ interest and motivating them to fully engage with the material. This is precisely the outcome achieved through Microlearning-based training.
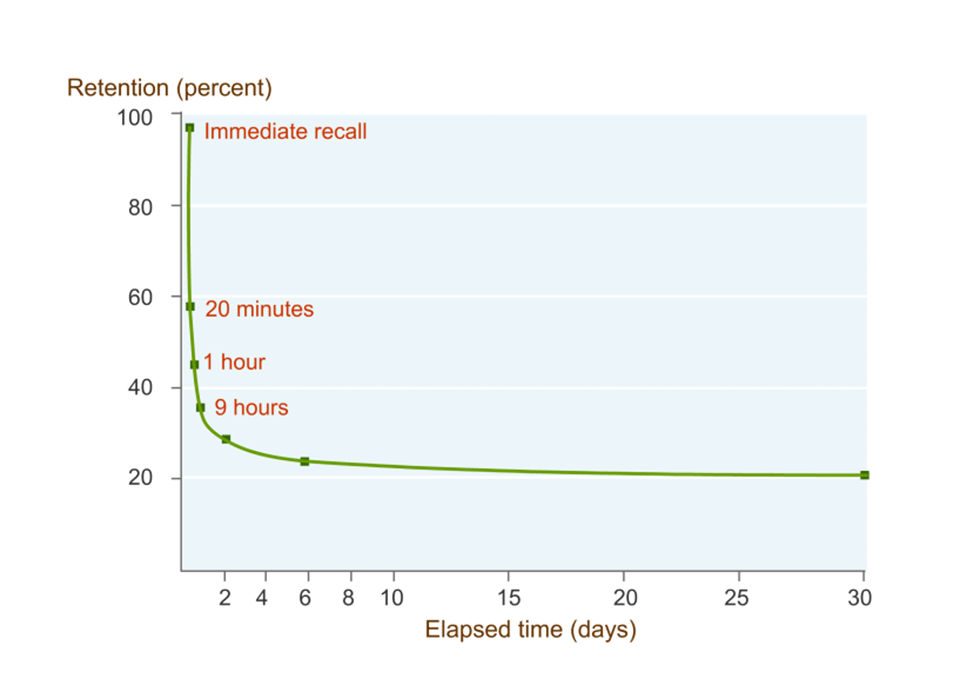
According to several studies, learners often lose 80% of what they may have learned in a 30-day period. Microlearning's learner-centric approach produces sticky learning experiences that enhance memory and retention. Additionally, it lets learners use what they’ve learned to increase productivity. In addition to serving to reinforce formal training, bite-sized learning also initiates behavioral changes for transformational gain and makes formal training accessible through Performance Support Tools (PSTs).
3
What are the Benefits of Microlearning?
In contrast to traditional approaches, Microlearning offers several significant advantages to both learners as well as businesses:
- Affordable and agile: Organizations need not spend exorbitant amounts of money on Microlearning nuggets. Studies reveal that organizations end up bringing down the development cost by 50% with Microlearning at a development speed of +300%.
- Shorter development cycle: As Microlearning nuggets are short, it doesn’t take long to build them. This short development cycle results in less expenditure and a quicker turnaround time for organizations.
- Easy to update: The short turnaround time factor comes into play in case updates have to be made to the nuggets as well. As they are short, it doesn’t take long to fix/update them, thereby providing organizations with an obvious advantage.
- Wider application: You can use Microlearning for both Formal and Informal Training needs. They offer you the flexibility to use them as Performance Support Tools (PSTs), as standalone learning nuggets, or as a part of a series of courses. You can also offer them through an LMS or integrate them in the learning path of a learning portal.
- High impact: As Microlearning nuggets help achieve a specific learning objective, they help create a high impact as learners get to learn exactly what they needed.
- Increased Employee Engagement and Retention: Microlearning's short, focused modules are more engaging for employees, leading to higher completion rates and better knowledge retention. Additionally, Microlearning's interactive nature encourages active participation, making learning more enjoyable and memorable.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency: With Microlearning, businesses can develop and deploy training content quickly and at a lower cost compared to traditional methods. The modular nature of Microlearning allows for easy updates and revisions, ensuring that content remains relevant and up-to-date without a significant investment of time or resources.
4
What are the Limitations of Microlearning?
Microlearning may not be suitable for scenarios characterized by lengthy and intricate training programs, especially those involving complex concepts and interrelated learning components. In such instances, it is more logical to present the training as a single comprehensive learning unit.
Dividing such content into multiple smaller nuggets could be counterproductive, leading to a fragmented learning experience and potentially diminishing the overall learning outcomes. In such circumstances, a Macrolearning-based approach would be the more appropriate choice over Microlearning.
Read More
- What Is Microlearning
- Top 10 Microlearning Trends To Adopt In 2024
- Why Adopt Microlearning – 15 Questions Answered
- Top 5 Benefits of Microlearning
- The Microlearning Solution: Is Microlearning Right For You?
- How to Blend Microlearning and Macrolearning to Deliver a Higher Impact Workplace Training
5
What are the Various Types of Microlearning You Can Use?
-
- 1. Infographics
They are a great fit to summarize the key takeaways. The visual approach to summarize the key aspects leads to higher recall and retention.
-
- 2. Interactive Infographics
Like infographics (in terms of visual-based approach), the interactivity enables you to layer information and pack more details. As an extension, they can be used as short learning guides.
-
- 3. PDFs
This is probably the most common format for microlearning and can be used to provide quick and just-in-time access to specific information.
-
- 4. Interactive PDFs
The more current avatar of the traditional PDFs, that allow longer reams of data to be packaged in meaningful info groups that the learner can browse through easily.
-
- 5. eBooks And Flipbooks
They make handy job aids wherein you can pack great visual appeal and interactivities. They are multi-device and can generate HTML5 output. You can also integrate audio and video to further enhance the impact.
-
- 1. Animated Videos
A popular format that can be adapted to create a variety of learning aids. It can also be a part of traditional eLearning (context-setting or learning summary).
-
- 2. Whiteboard Animation
A picture is worth a thousand words. Explaining concepts through pictures (featuring illustrations, animations, and audio) creates a high engagement, and the image stays with the learners well past the learning interaction.
-
- 3. Kinetic Text-based Animation
Sometimes, when minimalism scores instead of visuals, the animation of text (with sound effects) can be used to convey the required message.
-
- 4. Explainer Videos
As the name suggests, these are great to introduce a concept in an easy-to-understand visual manner. Sharp and focused, they can be aligned to meet a specific outcome very effectively.
-
- 5. Interactive Videos
While video-based learning is great, you can top it up through interactive video-based learning. You can add interactions (matching the learning interactions of eLearning courses) to create high impact learning experiences.
-
- 6. Expert Videos, Webinars/Recorded Webinar
We look forward to expert advice and insights. Using this approach makes them accessible to learners when they want to review or at the moment of their need.
-
- 7. Webcast/Podcasts
These are again very useful formats that can be accessed on demand by the learner at the moment of their need.
-
- 1. Interactive Parallax-Based Scrolling
Another very interesting format that uses the parallax approach that is commonly used in websites. It uses the same technique to simulate a learning path that the learner can “scroll through.” Alongside the learning path, interactions and quizzes can be added.
-
- 2. Mobile Apps
A very powerful approach to offer learning is through a mobile app that is being talked about as the “future of learning”, Not only is it the right fit for learning on the go; it brings in the added advantage of doing both online and offline viewing (when there is no internet access).
-
- 3. Complex Branching Scenarios
When you need to simulate complex, real-life situations that learners need to handle and gain mastery on, this format is the right fit.
6
Best Practices for Implementing Microlearning
To successfully leverage Microlearning, you must first understand their audience’s needs – including learning preferences, learning needs, and the learning challenges of hybrid learners – before developing short, action-oriented, learning nuggets for targeted outcomes. Then, package the content in ways that learners can readily apply it to their job.
Here are some tips and best practices to ensure you are using Microlearning the right way:
- Clear Learning Objectives: Begin by defining clear and specific learning objectives for each Microlearning module. What do you want learners to know or achieve after completing the module? Having well-defined objectives helps in creating focused and relevant content.
- Keep it Short and Focused: Microlearning should be brief and focused, typically lasting 3 to 5 minutes. Avoid overloading learners with information. Each module should address a single concept or skill to ensure clarity and retention.
- Design modular, small-footprint Microlearning content in the context of workflow. Ensure the content remains focused on specific (one or two) outcomes.
- Make the content “accessible”, so learners may consume it anywhere, anytime, and on any preferred device. Ensure content is intuitively hosted, so learners may quickly access them in the moment of need.
- Incorporate a diverse mix of content formats, including short videos, animations, eBooks, infographics, interactive quizzes, podcasts, summary PDFs, sample checklists, quick reference guides, and “How to…” content to enhance the learning experience. Visual and interactive content can make Microlearning more appealing and effective.
- Make sure formal training links extensively to your bank of Microlearning content, so learners may use them for review and refresher purposes.
- When designing formal ILT and VILT, make use of Microlearning as pre, during, and post learning content to help learners access optional and supplementary materials. This will reinforce their trust in such resources and help them explore and discover the power of microlearning as a performance enhancer.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Microlearning is often consumed on mobile devices, so ensure that your content is mobile-responsive and user-friendly. Use a format that works well on various screen sizes and orientations.
- Assessment and Feedback: Include assessments or quizzes at the end of each Microlearning module to gauge learner understanding. Provide immediate feedback to reinforce learning and address any concerns.
Remember that Microlearning is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Customize your approach to the specific needs of your learners and the objectives of your training program. By following these best practices, you can create Microlearning experiences that are engaging, effective, and beneficial for skill development and knowledge retention.
Read More:
- 24 Types Of Microlearning Content For Formal And Informal Learning In The Workplace
- 7 Microlearning Online training Assets You May be Overlooking
- 7 Obstacles to Avoid when Creating Microlearning Online Training Resources
- How to Use Microlearning To Train Your Multi-Generational Workforce
7
Top Microlearning Strategies
Microlearning is certainly more effective as an in-the-flow of work learning strategy because it happens through more focused content, which produces specific outcomes in a shorter timeframe. Organizations may use the following in-the-flow Microlearning strategies to create a culture of continuous learning – as just-in-time learning and to supplement formal learning:
- Immediate learning to support “in the moment” needs: Use Microlearning point-of-need training content, such as short podcasts or “How to” videos that serve as performance support aids.
- Intermediate learning to build existing competencies: Integrate Microlearning to complement formal training programs designed to improve employees’ performance in their current positions. These concise learning materials can also be effectively utilized as review and refresher training modules.
- Transitional learning to guide learners into future roles: Incorporate Microlearning nuggets throughout the in-person instructor-led training (ILT) or virtual instructor-led training (VILT) experience. These nuggets can be employed as training readiness tools for training, interactive exercises and assessments, and as a means to provide succinct learning summaries before, during, and after the training sessions.
- AI-driven personalization: With the rise of AI tools, personalization has gotten easier. AI can help organizations analyze learner profiles to assess the strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences to create personalized learning experiences. Machine learning algorithms can dynamically adapt content delivery and based on the learner’s performance adjust the difficulty of exercises accordingly.
- Predictive Analytics and AI: Predictive Learning Analytics (PLA) is a set of methods and technologies used to predict future learner outcomes. By identifying patterns and trends in past data, organizations can analyze which trainings will benefit learners. Some use cases of predictive analytics include personalized guidance, moment of need-based learning interventions based on learner progress and performance, smarter learning paths, and data-driven decision making.
- Automated Feedback and Support: Feedback loops based on performance can be generated using AI and generative AI, providing just-in-time feedback. This can free up time for L&D teams to focus on strategic initiatives. For example, integrating Open AI’s ChatGPT into an activity with a clearly defined validation criteria for accurate and personalized feedback.
- Virtual Assistants (VAs): VAs help provide just-in-time information and support, promoting learning in the flow of work.
- Engagement Tracking with AI: AI tools can analyze user interactions with interactive learning materials to effectively monitor and enhance learner engagement, adapt content delivery, adjust difficulty levels, and suggest supplementary resource materials for an optimized learning experience.
- Microlearning-based Learning Paths with AR/VR and AI: components for constant reskilling/upskilling. These formats will offer immersive, personalized learning experiences that captivate learners. By leveraging AR/VR technologies, learners will be able to engage in realistic simulations, fostering experiential learning. AI-driven algorithms tailor content delivery based on individual progress and preferences, ensuring relevance.
This dynamic combination will not only enhance learner engagement by offering interactive and engaging experiences but also promote active participation and knowledge retention, driving continuous learning in the workplace.
In a rapidly evolving work environment, employees often find themselves with limited time to dedicate to formal learning, while organizations are eager to gain any competitive advantage they can. Consequently, learning in the flow of work has emerged as the prevailing approach. Microlearning presents a mutually beneficial solution for seamless learning within the workflow, benefiting both employees and organizations. The three Microlearning strategies outlined here exemplify this win-win approach to learning within the workflow.
Read More:
- Power Triad – Using mLearning, Microlearning, and Gamification to Create Immersive
Learning Experiences - Microlearning Strategies to Promote Learning in the Flow of Work
- How to Build Employee Learning Habits and Drive Continuous Learning in the Workplace with Microlearning
- How to Offset the Forgetting Curve in Your Employee Learning Programs with Microlearning
- Change Employee Behavior in the Workplace with These 5 High-impact Corporate
Training Strategies - 6 Go-to Strategies to Transform Your Recorded VILT Sessions to Engaging Microlearning Modules
8
Examples of Microlearning
Below are some excellent real-world instances of microlearning in action in the corporate training world:
The purpose of this course was to create a sustainable, simplistic, on-demand training that volunteer trainers could use at their moments of need and incidentally learn concepts in the process.
- Used immersive microlearning formats
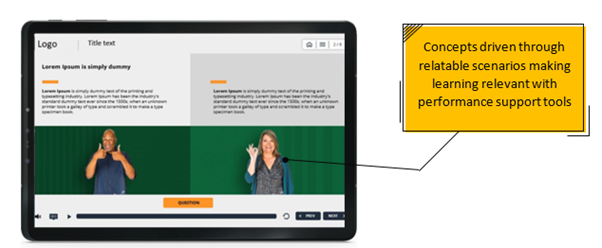
- Ensured relevance by using relatable scenarios
- Promoted an immersive experience through video and podcast-based activities
- Boosted learners’ confidence to facilitate live sessions
The purpose of this course was to build a comprehensive series of leadership trainings to equip and empower leaders in developing themselves and their teams successfully.
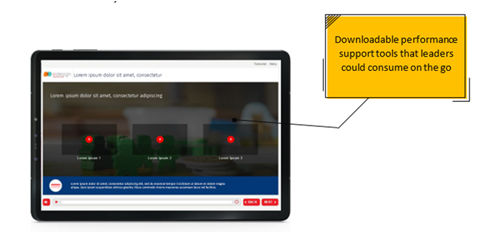
- Ensured just-in-time learning using appropriate formats such as relatable practice scenarios, interactive learning elements, and downloadable performance support tools
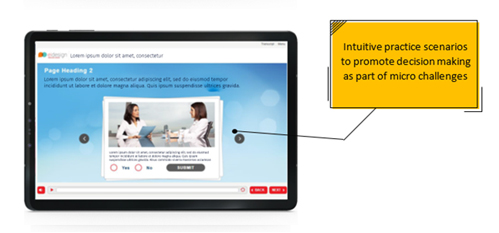
- Promoted decision making as part of micro challenges through intuitive business scenarios
- Improved performance ensured higher participation and completion rates
The purpose of this course was to familiarize employees with their organization’s culture, vision, mission, and values in a consistent and impactful manner while pushing a steady behavioral change.
- Employed a portal-based microlearning method for easy access
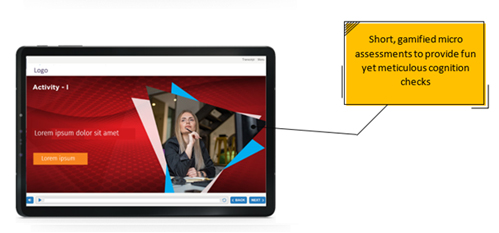
- Introduced gamified micro activities for cognition checks and practice through fully mobile responsive designs
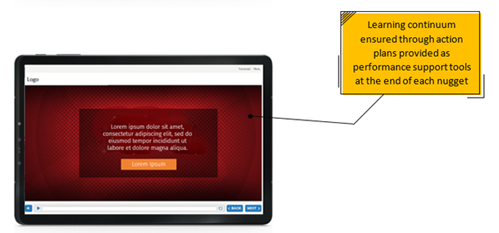
- Provided action plans at the end of each nugget to ensure continuum
- Employees demonstrated behavioral aspects of the organization’s culture as a result of the training
A unique microlearning program was created for an FMCG giant that transforms the way their leaders perceive a crucial process like mentoring.
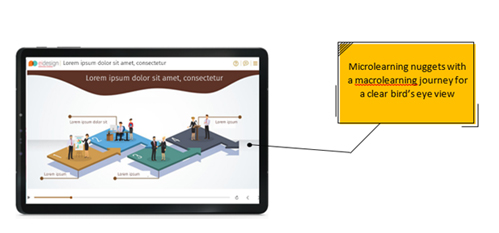
- Featured short, succinct concepts for effective learning by employing ‘microlearning within a macrolearning path’
- Used crisp analogies to convey concepts
- Provided infographics and iPDFs as takeaways or job aids
- Leaders applied mentoring concepts effectively thus boosting enrollment in mentorship program
The primary objective of the training program was to acquaint newly onboarded employees with the IT department’s operations and to provide them with a comprehensive understanding of commonly used collaboration tools and resources. Additionally, the training aimed to raise awareness among participants about fundamental aspects of information security.
- Employed various microlearning formats, including videos, concise scenarios, interactive activities, and a gamified assessments
- Adopted a mentor-mentee approach which created highly immersive experiences
- An activity-driven approach ensured “learning by doing”
- Used relatable personas to make the experience immersive to learners
9
Parting Thoughts
In conclusion, this page has provided a comprehensive exploration of Microlearning, from its definition and theoretical foundations to its practical benefits and limitations. We’ve delved into when to use Microlearning, its various types, and best practices for implementation. When coupled with AI, this approach has the potential to completely transform learning by offering learners more engaging, adaptive content. Future advancements, such as AI-driven personalization, predictive analytics, and immersive technologies like AR/VR, will further amplify the effectiveness of Microlearning. Moreover, we’ve shared some top Microlearning strategies and real-life examples to illustrate its effectiveness.
As we wrap up our journey through the world of Microlearning, it’s crucial to remember that this efficient learning approach can be a valuable addition to your training program. It offers the flexibility and adaptability needed to meet the diverse needs of learners in today’s fast-paced world.
We hope this page has equipped you with the knowledge and insights necessary to harness the power of Microlearning effectively. If you have any remaining questions or need further guidance, don’t hesitate to explore our FAQs section or reach out for additional support.